Page 52 - TRI
P. 52
ANNUAL REPORT 2023-24 TRANSFORM RURAL INDIA
TRI is engaged intensively in three states planning tools in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra
further mentioned in the report on landscape facilitated more accurate and effective
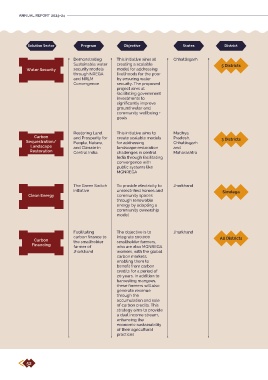
Solution Sector Program Objective States District Restoration and improving government landscape management plans. In Maharashtra,
planning and allocation systems to increase the use of Kobo Forms helped in collecting
demand and convergence of other extensive community demands, showcasing an
Demonstrating This initiative aims at Chhattisgarh
Sustainable water creating a scalable 5 Districts departments for restoring land, people and innovative approach to participatory planning.
Water Security security models model for addressing nature. The core focus of the engagement in
through NREGA livelihoods for the poor the last year was on MGNREGA. In the Carbon Financing solution sector, the
and NRLM by ensuring water
Convergence security. The proposed • Increased Demand in Labour Budget Intellecap -TRI- Rabobank program in
project aims at Planning for NRM: In Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand aims to ensure the survival and
facilitating government maintenance of fruit tree and agro-forestry
investments to collaboration with WRI led to the plantations established under the Birsa Harit
significantly improve development of VPRP , generating demand
ground water and for over 24,629 landscape restoration works Gram Yojana (BHGY) by connecting them to the
community wellbeing + and securing a budget of INR 145 Crore global carbon market. This initiative is designed
goals to provide additional income to the smallholder
focused on NRM. Chhattisgarh and
Maharashtra also saw significant budget farmers of Jharkhand without requiring any
Restoring Land This initiative aims to Madhya submissions for landscape restoration, investment from them or the government. By
Carbon and Prosperity for create scalable models Pradesh, leveraging carbon credits, the program
Sequestration/ People, Nature, for addressing Chhattisgarh 3 Districts approximately 293 Crores of plans in supports environmental sustainability and
Landscape and Climate in landscape restoration and Maharashtra and 64 Crores in Chhattisgarh,
Restoration Central India challenges in central Maharashtra reflecting an improved planning process and enhances the economic stability of local
India through facilitating enhanced demand at the district level for farmers by ensuring they receive fair
convergence with climate actions. compensation for their contributions to carbon
public systems like sequestration, ultimately fostering a
MGNREGA • Convergence with Government sustainable agricultural environment in the
Departments: TRI has established region. The objective is to integrate 100,000
The Green Switch To provide electricity to Jharkhand convergence frameworks with multiple smallholder farmers, who are also MGNREGA
initiative unelectrified homes and Simdega departments like MGNREGA, Tribal, workers, with the global carbon markets,
Clean Energy community spaces Agriculture, and Forest departments across
through renewable enabling them to benefit from carbon credits
energy by adopting a the states. These frameworks support the for a period of 20 years. In addition to
community ownership resource envelope needed to back the harvesting mangoes, these farmers will also
model landscape restoration plans and are pivotal generate revenue through the accumulation
in the integrated approach to sustainable and sale of carbon credits. This strategy aims to
landscape management. provide a dual income stream, enhancing the
Facilitating The objective is to Jharkhand
carbon finance to integrate 100,000 • Demonstration and Scaling of Projects: TRI economic sustainability of their agricultural
Carbon the smallholder smallholder farmers, All Districts has set up demonstration sites in key practices
Financing farmer of who are also MGNREGA districts of Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and
Jharkhand workers, with the global TRI is forging new partnerships in the climate
carbon markets, Madhya Pradesh, showcasing effective
enabling them to decentralized planning and watershed sector and linking agriculture, technology, and
benefit from carbon management. These demonstrations are clean energy in India. Collaborating with the
credits for a period of planned to be scaled up in the following India Climate Collaborative and joining the India
20 years. In addition to Agri Voltaic Alliance (IAA), TRI supports building
harvesting mangoes, financial year, potentially enhancing
these farmers will also landscape restoration efforts across broader scalable agri-photovoltaic models for small
generate revenue areas. In Madhya Pradesh, the efforts are and marginalized farmers. Leveraging its
through the already getting results as the MPGEC has extensive experience in rural sectors and
accumulation and sale integrative technology solutions, TRI is
of carbon credits. This asked to submit plans to take up similar
strategy aims to provide effort to 55 districts of Madhya Pradesh. establishing a learning network for women
a dual income stream, farmers to connect with ecosystem service
enhancing the In the climate action programs of TRI, providers. The focus is on using public
economic sustainability
of their agricultural specifically in Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand and investments to pilot agri-photovoltaic systems
practices Maharashtra various technology introduction tailored to the grassroots needs of small and
are done to improve the efficiency of the marginalized women farmers.
programs. The introduction of GIS-based
52 53